
What is blue light?
We already know about the blue light emitted by artificial sources with LED or compact fluorescent lamps such as computer screens, smartphones, etc. but blue light is a light mainly emitted by the sun.
The light intensity of the sun can be 1,000 times greater than that of screens and you would have to spend 64 full days in front of your digital tablet for the equivalent of one hour of sun exposure.
It is therefore necessary to protect the skin from the blue light of the sun.
Understanding blue light and its effects
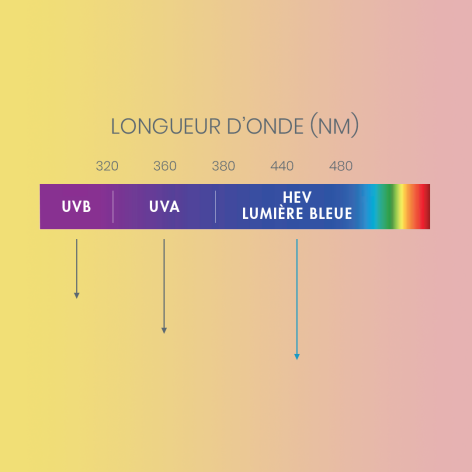
“Blue-violet” light is the band of the visible spectrum containing the most energy, hence its name HEV for "High Energy Visible Light" which is harmful to the body: it accelerates the ageing of our cells and we need to protect ourselves from it.

Playing YouTube videos requires the use of cookies in order to offer you targeted advertising based on your browsing For more information, please visit YouTube's « cookie » policy.
You have rejected Youtube's cookies and therefore you cannot view the video.
You can change your choices by clicking on « Cookie Settings » and accept Youtube's cookies to enable the video.
You can change this setting and withdraw your consent at any time.
25% of cell damage is caused by blue light. Its radiation accelerates the ageing of the skin every day and encourages the appearance of wrinkles and spots
Therefore, it’s reasonable to assume that in the long term, and especially as ageing erodes cellular defence mechanisms, exposing the skin to high-energy light can have a harmful effect that increases the ageing process and even has cancerous mechanisms. In addition, blue light acts on the pigmentation gene and stimulates the activity of melanocytes. This aggravates certain dermatoses linked to the functioning of melanin, such as pregnancy mask or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Blue light therefore has potentially even more devastating effects than UVA, especially on darker skin.
With blue high-energy visible light, a new skin enemy has been discovered, perhaps even more harmful than UVA and UVB. These harmful rays penetrate even deeper into the skin layers, reaching the hypodermis. With its intense energy - which gives it its name - blue light attacks all cellular constituents: lipids, proteins and DNA. These rays alone damage the skin cells in one hour of sun exposure². Other studies have also shown that this blue-violet light leads to the formation of toxic reactive oxygen species that affect all the constituents of skin cells: lipids, proteins and DNA.

Playing YouTube videos requires the use of cookies in order to offer you targeted advertising based on your browsing For more information, please visit YouTube's « cookie » policy.
You have rejected Youtube's cookies and therefore you cannot view the video.
You can change your choices by clicking on « Cookie Settings » and accept Youtube's cookies to enable the video.
You can change this setting and withdraw your consent at any time.
NEWSLETTER
We're always here for your skin!
All our tips on how to take care of your skin every day.
Which skin care routine should you adopt?
Identify what it really needs with the help of our experts and discover the most suitable skin care routine for you.
