What exactly is sunburn?
Sunburn (or solar erythema) is an inflammatory response of the skin caused by exposure to UVA and UVB radiation. It is accompanied by redness, a painful sensation of heat and itching which, in the most severe cases, can lead to blisters. Sunburn can also leave scars on the skin. Its severity varies according to skin type and phototype, individual UV sensitivity, genetic factors, duration and frequency of exposure and the intensity of solar radiation.
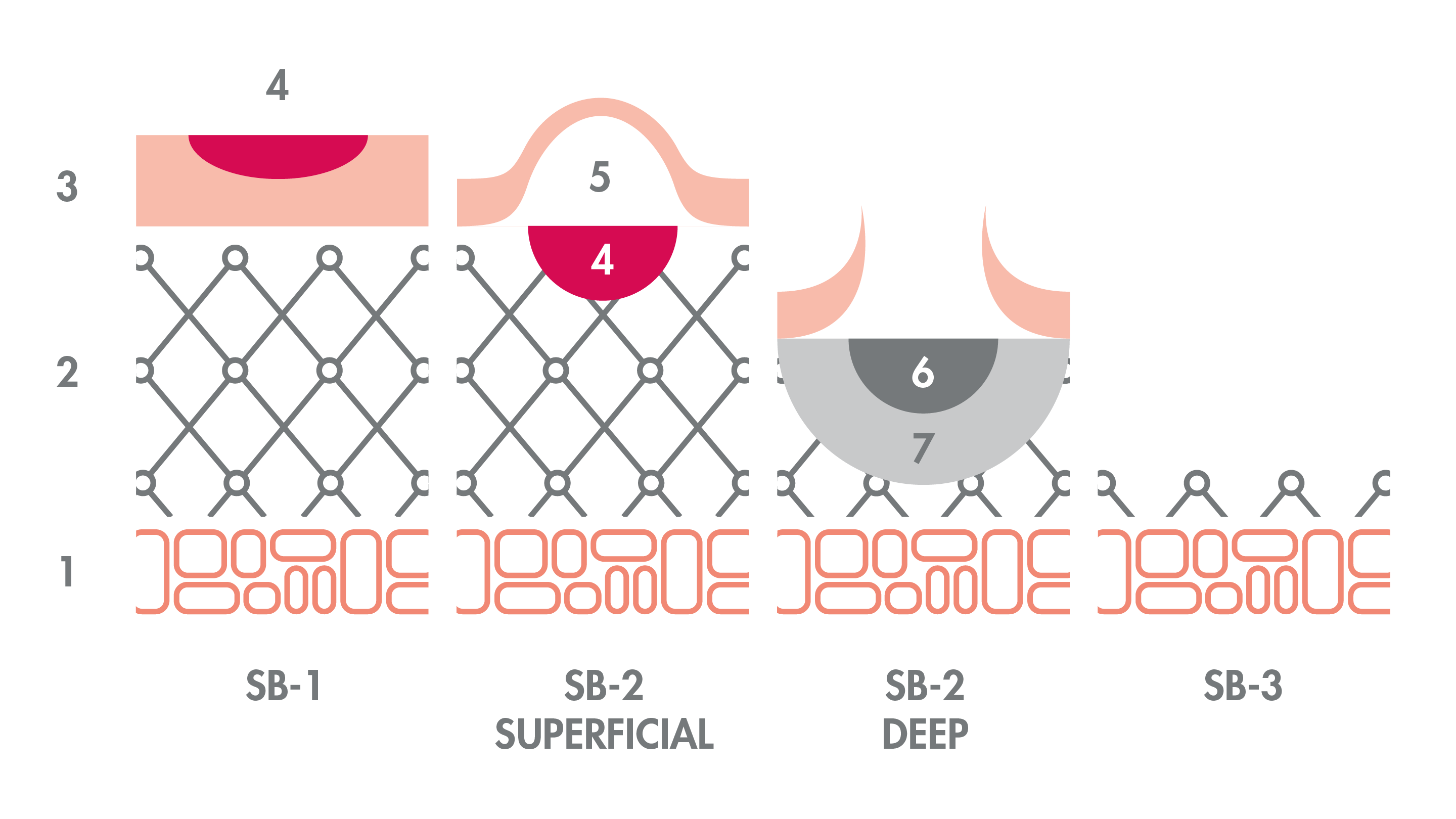 1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis - 3: Epidermis - 4: Redness - 5: Bumps - 6: Discoloured dermis - 7: Mild pain
1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis - 3: Epidermis - 4: Redness - 5: Bumps - 6: Discoloured dermis - 7: Mild pain
The three types of radiation from the sun
Direct radiation
Varies according to altitude, latitude, season and time of day
Diffuse radiation
Dispersed by atmospheric components, such as clouds,
mist and dust particles
Reflected radiation
From surfaces; varies according to how reflective the surface is (snow, sand, sea, grass, etc.).
Together, direct, diffuse and reflected radiation are called total solar radiation.

If you have a headache or fever in addition to your sunburn, you may be suffering from sunstroke. In this case, seek advice from a pharmacist or doctor. Symptoms may become more severe within 2 days of sunburn, but will subside within a few days.
The different forms of sunburn
Solar erythema consists of four stages of more or less deep burns.
First degree burns
A first degree burn is a simple erythema: the skin is red, dry and painful. This is the case, for example, of superficial sunburn without blisters or scaling, where only the epidermis is affected. Complete healing of the first degree burn takes an average of one week and will not leave a scar on the skin. You can help your skin to heal by moisturizing it regularly.
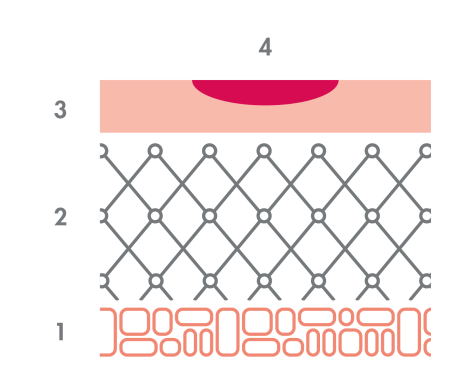 1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis - 3: Epidermis - intact skin - 4: Redness
1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis - 3: Epidermis - intact skin - 4: Redness
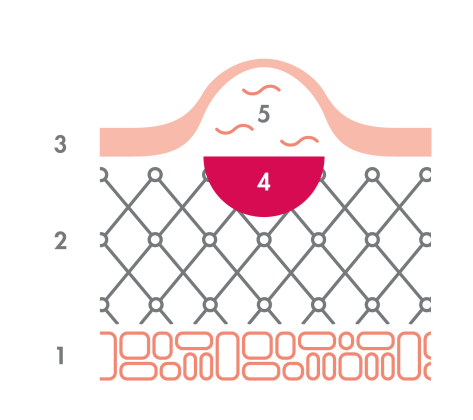 1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis - 3: Epidermis - 4: Redness - 5: Bumps (phlyctenes)
1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis - 3: Epidermis - 4: Redness - 5: Bumps (phlyctenes)
Superficial second degree burns
Superficial second degree burns are characterised by the appearance of red blisters filled with a clear liquid immediately or within hours of the burn. The dermis is affected. The skin is ultra-sensitive to touch, and even contact with clothing becomes painful. Healing takes 2 to 3 weeks and the burn does not leave a skin scar. To facilitate healing, remember to disinfect and moisturise your skin.
Deep second degree burns
Blisters are usually pierced. Under these blisters, the dermis is discoloured and the pain is mild because the skin is as if "anaesthetised". While in the superficial second degree burn the dermis is red and sensitivity is retained, the blood vessels have been destroyed in this burn. This type of burn requires medical attention. Healing usually takes 2 to 3 weeks, with a more or less discrete scar.
 1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis - 3: Epidermis - 4: Discoloured skin - 5: Mild pain
1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis - 3: Epidermis - 4: Discoloured skin - 5: Mild pain
 1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis
1: Hypodermis - 2: Dermis
Third degree burns
The skin feels like cardboard, is white or brownish in colour, loses sensitivity and the hairs are burnt. The dermis is affected, sometimes even the hypodermis, in which case there is a risk of infection. Bright red marks with oedema appear between 2 and 6 hours after exposure and end with severe exfoliation and long-lasting pigmentation. This stage requires emergency treatment, usually in hospital.
FRIENDLY, EXPERT ADVICE
Beware of sunstroke
If you have a headache or fever in addition to your sunburn, you may be suffering from sunstroke. In this case, seek advice from a pharmacist or doctor. Symptoms may become more severe within 2 days of sunburn, but will subside within a few days.
How to get rid of sunburn
It takes about a week for sunburn to heal with a peeling phase. Sunburn may take longer to disappear if it's causing blisters and many blood vessels have been destroyed. Healing can take between two weeks and a month, and the burn may leave spots or scars on the skin.

How to relieve sunburn
If you have a simple burn, there are a few things you can do to help soothe your skin:
- Don’t go out in the sun at all (no matter how bad the sunburn is!) and stay in the shade
- Drink plenty of water to combat dehydration
- Apply soothing after-sun creams to sunburnt areas
- Refresh the burnt area with cold water
- If blisters occur, they should not be punctured and should be covered with a sterile dressing
- Monitor your temperature
- In case of headache or fever, take paracetamol.
If the burn is more severe, with deep second-degree or third-degree symptoms such as blisters and a paradoxical lack of pain, consult your doctor as soon as possible.
FRIENDLY, EXPERT ADVICE
How to "put out the fire" after sunburn?
- Start with an Avène Thermal Spring Water compress. To make your compress, soak some tissue in Avène Thermal Spring Water, apply it to the affected area and leave for 15 minutes, spraying the area regularly with Thermal Spring Water.
- Store your Avène Thermal Spring Water Spray in the fridge to increase its refreshing effect
- Take some After-Sun Restore in your hands and apply it to the skin by laying your hands flat on your body and face, without rubbing.
Consequences of repeated sunburn on the skin
No matter how intense the sunburn, it can have serious long-term consequences. The skin remembers everything, and repeated sunburns can be permanently imprinted on your skin like on a camera film, sometimes to the point where it can’t be restored. This is why it’s essential to choose appropriate sun protection and to scrupulously follow the rules of sun exposure to prevent the risks of skin cancer.

The risks of skin ageing
The sun is a factor in accelerated skin ageing just like smoking. UVB rays cause the epidermis to thicken, while UVA rays destroy the connective tissue of the skin and cause a loss of elasticity and hydration capacity. Wrinkles, puffiness and brown sun spots are all signs of premature skin ageing. However, when the skin has thickened, tanning is more difficult: the skin's melanocytes are less reactive because they have also undergone premature ageing, and sunburn is more painful because the skin is drier. It’s a vicious circle that should be broken as soon as possible by protecting the skin from the sun from a very young age.
The skin is left fragile
After a sunburn, the skin should be allowed to take a breather and wait a while before being exposed to the sun again. Sunburnt skin is fragile and will be more sensitive to all external factors: cold, wind and salt, are all elements that can attack the skin.
The skin has a memory: it becomes imprinted just like the film of a camera, and sunburn can leave marks.
The risk of skin cancers
Overly frequent exposure to UVA rays can lead to an irreversible change in the genetic make-up of the skin cells, which then multiply at high speed causing a tumour. There are several types of skin cancer caused mainly by the sun, the most serious of which is melanoma.
Sunburn: We answer your questions
Stay out of the sun (wear a hat, sunglasses and use a parasol) and apply after-sun cream every evening to relieve the pain.
Sunburn is 80% UVB and 20% UVA.
Melanin is the skin's natural photoprotection against UV rays (that's why tanned skin is better at blocking UV rays than white skin). But this protection is limited: beyond a certain level of radiation, the skin can still burn. Even if you have a tan, it is important to continue protecting your skin by using a sun cream with a high SPF.
Second degree burns trigger a tan. But at what cost? Unsightly blisters, the risk of depigmentation, pain, premature skin ageing... For first-degree burns, however, this is not true: within a few hours or days, your skin will simply return to the way it was before.
Sunburn can never be considered as a preparation for tanning, and you shouldn’t go out in the sun after a sunburn. Although a sunburn sometimes gives way to a tan after a few days, it can also cause permanent pigment spots.
THE SOLUTION FOR SOOTHING SUN-DAMAGED SKIN
- Avène Thermal Spring Water SprayBest SellerAvène Thermal Spring Water SpraySoothes - Restores the skin barrier - Calms
- Cicalfate+ Restorative Protective CreamBest SellerCicalfate+ Restorative Protective CreamSoothes - Restores - Purifies
NEWSLETTER
We're always here for your skin!
All our advice on how to take care of your skin day to day.
Which skin care routine should you adopt?
Identify what it really needs with the help of our experts and discover the most suitable skin care routine for you.


